A Machine Learning (ML) approach was integrated with DNA-encoded chemical library (DECL) screening to facilitate the identification of highly selective compounds targeting Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) compared to its counterpart, HO-2 (the ferric-heme bound form, Holo HO-2).
HO-1 and HO-2 are principal enzymes within the HO family, known for their roles in inflammation and oxidative stress regulation. HO-1, particularly, has garnered attention for its potential as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammatory diseases. Furthermore, elevated levels of HO-1 have been observed in various cancers, including prostate, renal, colon, lung, breast, and glioma, often correlating with poor prognosis. Consequently, the development of selective HO-1 inhibitors holds significant promise for cancer therapy.
Initially, an affinity-based DECL screening campaign towards HO-1 was performed, incorporating selections in the presence of known inhibitors or allosteric binders, alongside counter-target selection (i.e., against HO-2). Subsequently, the resulting dataset underwent analysis and preprocessing to train a Deep Learning Model for virtual screening across commercially available libraries.
The virtual screening identified 392 compounds exhibiting a diverse structural distribution, with only partial overlap with the training compounds. This suggests that the proposed workflow can extend its reach beyond the initial DECL chemical space.
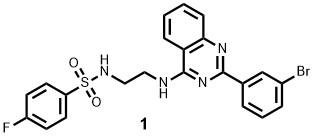
From the top 50 compounds identified by the machine learning model as potential high-affinity binders, 32 were subjected to further validation using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) binding analysis. Among these, 8 compounds demonstrated selective binding to HO-1 over HO-2, with binding affinities (KD) ranging from 141 nM (Compound 1) to 11 μM.
Considering the structure and physiochemical properties of these validated compounds, a subsequent virtual screening focused on molecular similarity was conducted within the same commercial libraries. This effort yielded an additional 11 analog compounds, which were further validated via SPR affinity analysis. Of these, 7 selectively bound to HO-1, with KD values ranging from 692 nM to 20 μM, while one compound exhibited promiscuous binding to both HO-1 and HO-2 (17 μM and 21 μM, respectively), and three compounds showed no activity.
Pooling all validation results enabled a preliminary Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) analysis for certain series of the newly discovered ligands.